Audit
Creating an Audit Time Series
By means of the audit function it is possible to archive time series data.
To create an audit time series, you must ensure that an archive table is specified in addition to a data table when you create the time series. This can easily be done by checking the "Archive" checkbox:
Reading Data of an Audit Time Series
The archived data of a time series can be read out via the time series plug-in or by entering the audit date in the worksheet.
Reading via the Time Series Plug-in
In order to use the audit options the "Parameters" section has to be expanded:
Using the drop-down list "Audit" in the time series plug-in you can read out the data of a time series at an earlier time.
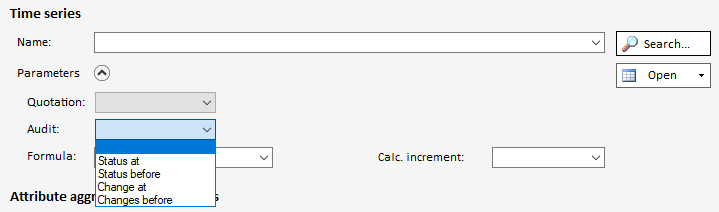
If you select an option here, a further drop-down list shows all the times at which data was saved in the selected time range (from - to). Of course, the date and time can also be set to a time that was not available for selection.
With the "Status before" and "Changes before" options, the number of the most recent changes to be loaded for the selected time series can also be specified. If there are fewer changes for a time series than specified using this option, all changes of this time series will be loaded, but not more.
The options "Status at" and "Status before" provide the time series data "not exact".
The options "Changes on" and "Changes before" provide the time series data "exact".
Reading via the Worksheet
An audit date can be specified in row 12 of a worksheet. This can be done in the form of the ISO-8601 standard, as well as in the form MM.dd.YYYY hh:mm:ss [AM|PM] (if the language in TSM is set to English). Furthermore you have to specify, if you want to read the date exact or not exact.
The two formats are equivalent and will provide the same data.
Difference Between Exact and Not Exact
For an exact audit time, data is only displayed if it was saved at exactly this time. If the audit time is not exact, the system checks for all non-existent values whether there is an earlier audit time and, if so, displays its values:
In the graphic above, the same time series is read out at two different audit times. The following can be seen:
- In column C you can see that on this time series on 7/7/20 at 11:38:53 AM the data in the rows below were saved. This can be recognized by the "exact" option.
- In column D you can see that no data was saved on the same day one second later. The "exact" option was used here as well.
- In column E you can see the same data as in column C, even though they were read from the audit time as those in column D. Therefore, the data that was last saved before the time entered in row 12 is displayed.
Saving Data on an Audit Time Series
If an audit date is specified, no data can be saved, as this function is only used to archive data. However, data can be saved without specifying a date (as with "normal" time series).
If data is saved on an audit time series, the time of saving is entered into the database as the audit time. This new time is then also available in the drop-down list.
